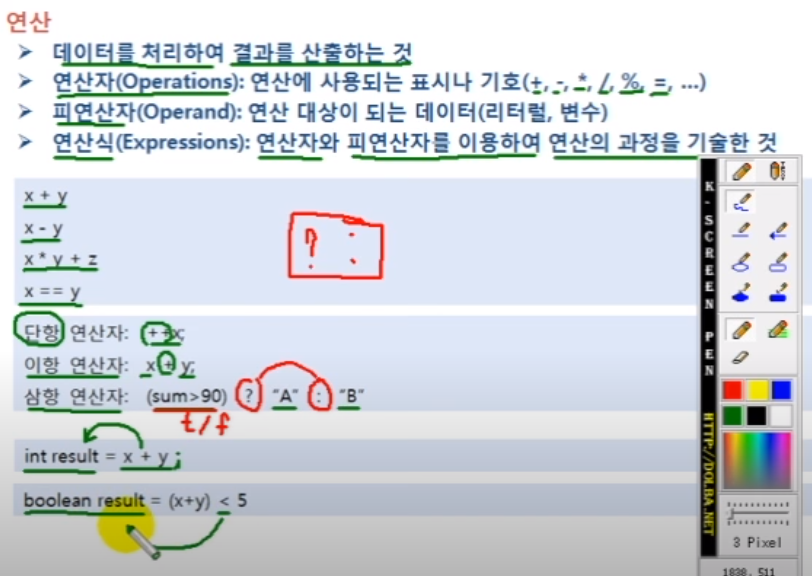
삼항 연산자 : 조건이 만족하면 "A", 아니면 "B' 출력


- 단항일 때 +,- 연산자를 사용하면 int타입으로 변환하여 저장됨.
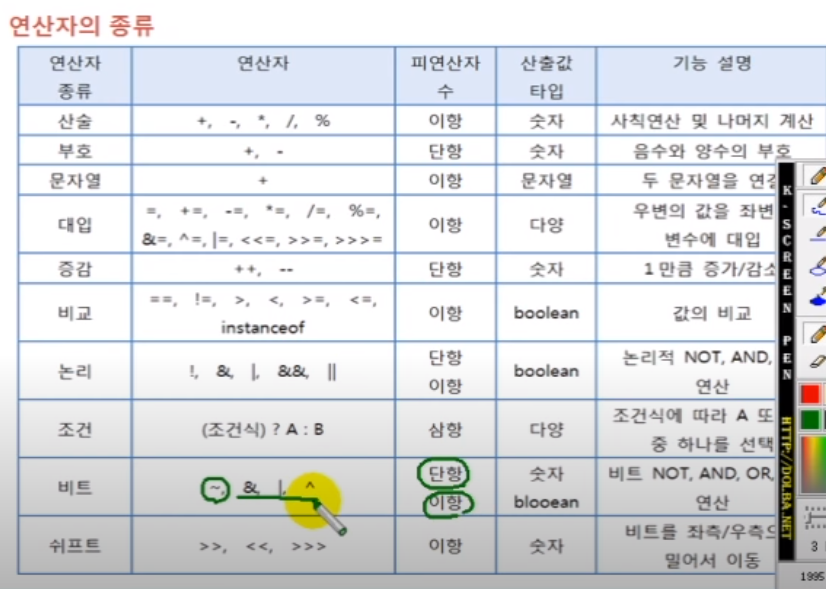
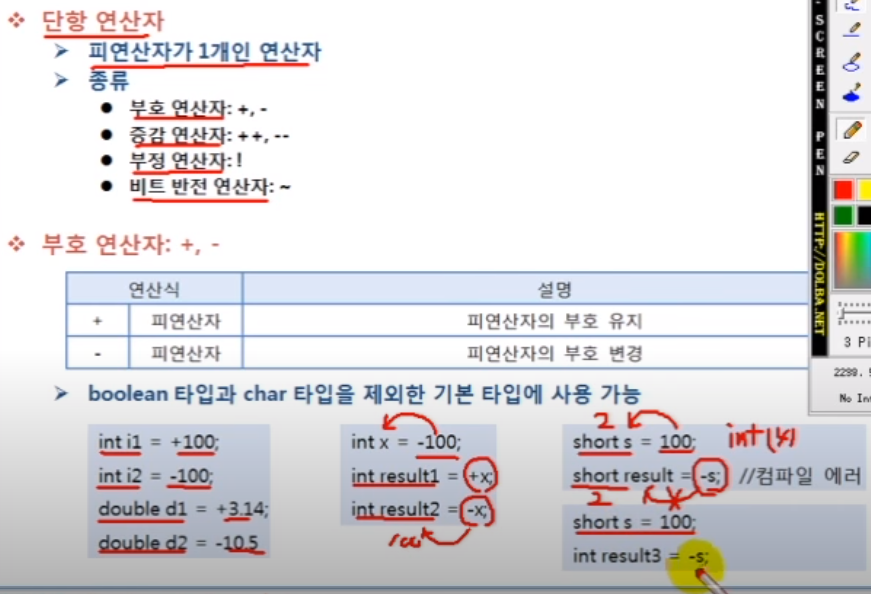
3.3 단항 연산자
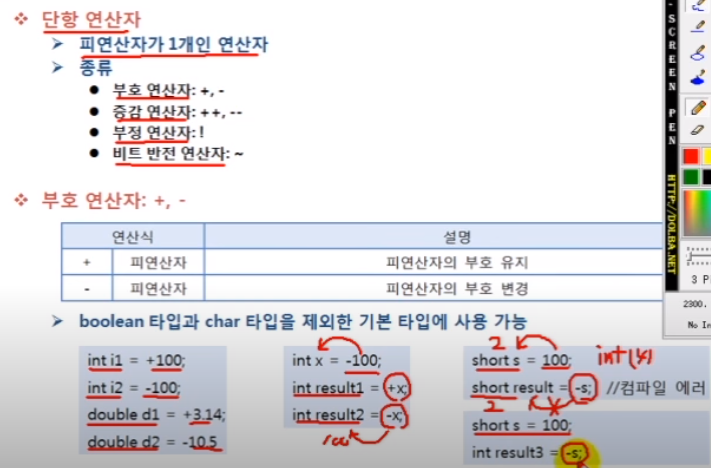
short에 100을 저장해도 int로 자동변환되서 저장됨.
int x = -100;
int result1= +x;
int result2 = -x;
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
short s = 100;
//short result3 = -s; //부호 연산자가 붙으면 값은 int로 변경
int result3 = -s;
System.out.println(result3);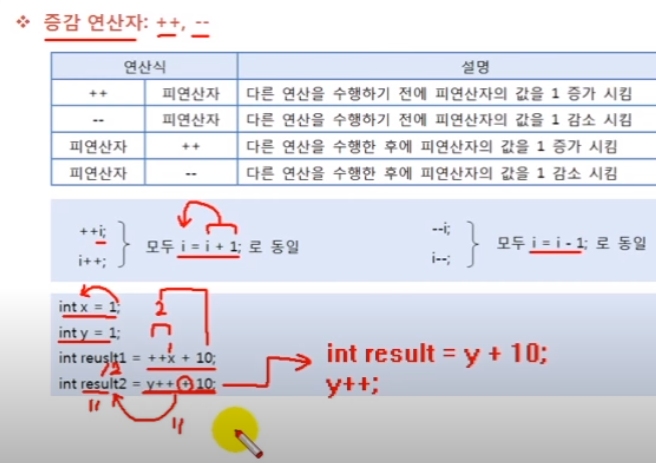
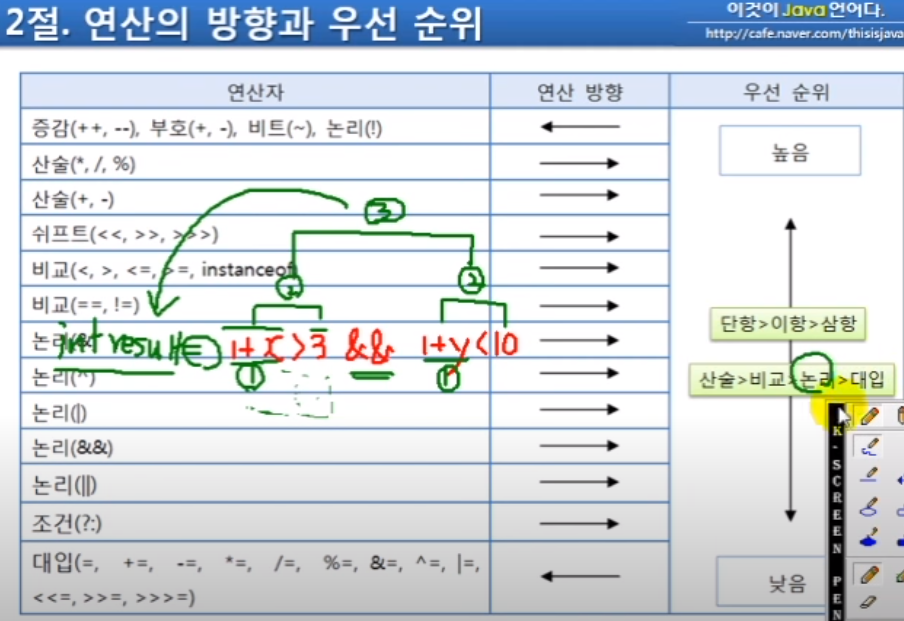
증감연산자와 산술연산자가 함께 쓰이면 증감연산자가 앞에 있느냐 뒤에 있느냐에 따라
연산자 우선순위가 다르게 나타남. 증감연산자가 앞에 있으면 먼저 증감한 뒤 산술하고
뒤에 있으면 산술연산자 먼저 처리한 뒤 증감연산자 처리함.
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
int z;
System.out.println("-------------");
x++;
++x;
System.out.println("x=" +x); //값은 x=12
System.out.println("-------------");
y--;
--y;
System.out.println("y=" +y); //값은 y=8
System.out.println("-------------");
z = x++;
System.out.println("z=" +z); //결과값은 z=12, 원래 x값이 z에 저장된 후 출력. 증감연산자는 그 후에 계산
System.out.println("x=" +x); //결과값은 x=13, 증감연산자가 반영된 값 출력
System.out.println("-------------");
z = ++x;
System.out.println("z=" +z); //결과값은 z=14, 증감연산자 계산 후 출력
System.out.println("x=" +x); //결과값은 z=14,
System.out.println("-------------");
z = ++x + y++;
System.out.println("z=" + z); //값은 23, x 먼저 증감하여 15 + 8 =23, 출력한 후 y증감
System.out.println("x=" + x); //값은 증감하여 15
System.out.println("y=" + y); //값은 모든 계산 이후 증감하여 9
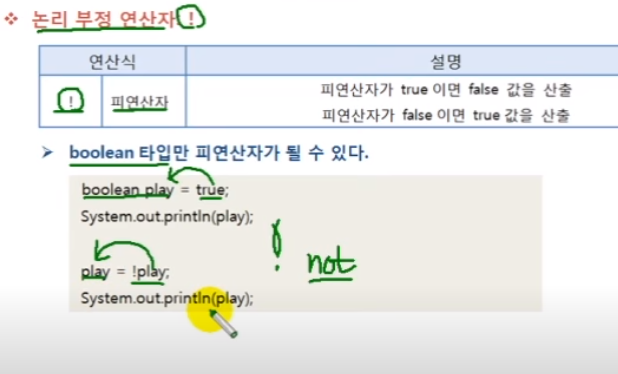
boolean play = true;
System.out.println(play); //값은 true
play = !play;
System.out.println(play); //값은 false
play = !play;
System.out.println(play); //값은 true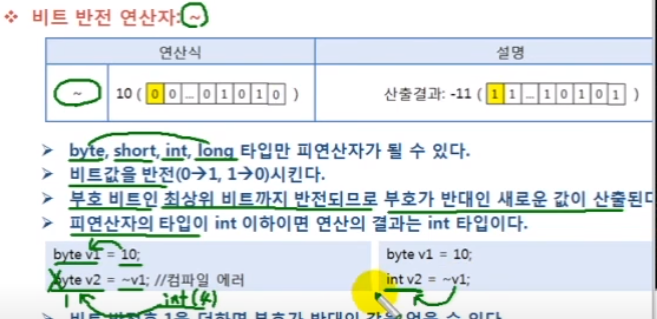
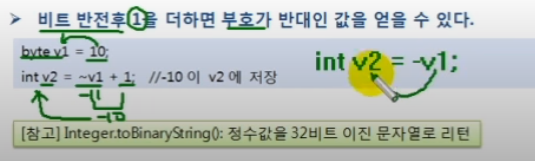
비트 반전 연산자 = ~
int로 변환되어 저장되므로 반드시 int로 받아야 함.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int v1 = 10;
int v2 = ~v1;
int v3 = ~v1 + 1;
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v1) + "(십진수:" + v1 + ")");
//값은 00000000000000000000000000001010(십진수:10) , int는 4바이트라서 32비트로 표현
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v2) + "(십진수:" + v2 + ")");
//값은 11111111111111111111111111110101(십진수:-11), 2진수로 표현된 값을 반대로 출력
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v3) + "(십진수:" + v3 + ")");
System.out.println(v2); //값은 -11
System.out.println(v3); //값은 -10
int v4 = -10;
int v5 = ~v4;
int v6 = ~v4 + 1;
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v4) + "(십진수:" + v4 + ")");
// 11111111111111111111111111110110(십진수:-10)
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v5) + "(십진수:" + v5 + ")");
// 00000000000000000000000000001001(십진수:9)
System.out.println(toBinaryString(v6) + "(십진수:" + v6 + ")");
// 00000000000000000000000000001010(십진수:10)
System.out.println(v5); //값은 9
System.out.println(v6); //값은 10
}
public static String toBinaryString(int value) {
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(value);
while(str.length()<32) {
str = "0" + str;
}
return str;
}
}비트 반전 연산자는 하드웨어의 제어 목적이 아니라면
웹애플리케이션, UI, 앱애플리케이션을 만든다면 잘 이용되지 않는다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| eclipse open project has encountered a problem 해결과정 (0) | 2021.03.27 |
|---|---|
| 이것이 자바다 (다섯번째 정리) - 3.4 이항 연산자(3) 초반까지 (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| 이것이 자바다 (세번째 정리) 2장 확인문제까지 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| 이것이 자바다 (두번째 정리) 2장 변수(2)까지 (0) | 2021.03.06 |


